PART II
[45 marks]
Answer anythreequestions from this section
-
(a) (i) Define respiration.
(ii) Give two differences between photosynthesis and respiration.
(b) (i) List the chemicals used in the preparation of carbon dioxide in the laboratory
(ii) How would you test for carbon dioxide in the laboratory?
(c) (i) State four effects of a force on a body.
(ii) A horizontal force of 250 N is applied to pull a piece of wood lying on a smooth surface through a distance of 20 m. Calculate the work done.
-
(a) (i) Give two differences between a vein and an artery.
(ii) State two functions of red blood cells.
(iii) Mention two diseases associated with the circulatory system.
(b) (i) Classify the following processes into a physical change and a chemical change:
Cooking of food;
Melting of candle;
Melting of ice;
Rusting of iron;
Dissolution of sugar in water;
Burning of wood into ash.
(ii) Explain the basis of the classification in (b)(i).
(c) (i) State the laws of reflection.
(ii) Draw a ray diagram of light incident at an angle of 40o on the surface of a plane mirror.
-
(a) (i) Explain vegetative reproduction
(ii) State two differences between sexual reproduction and vegetative reproduction.
(iii) Give one advantage of vegetative reproduction.
(b) (i) Name suitable solvents for the following substances:
oil paint, fat, common salt, plant pigments.
(ii) What is the name given to a substance dissolved by a solvent?
(c) The diagram below represent a simple machine.
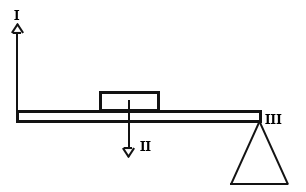
(i) What class of simple machine does it represent?
(ii) Name the parts labelled I, II and III
(iii) Give two examples of machines used in everyday life which work on the same principle as the system illustrate above.
-
(a) (i) Give two differences between a parasite and a vector.
(ii) Write down the names of three endo-parasites and their hosts.
(b) An atom has eight protons and nine neutrons.
(i) Draw the atomic structure of the atom.
(ii) If the atom gains two extra electrons what will be the charge of the ion formed? (Show working)
(c) (i) Three insoluble liquids X, Y and Z are shaken together in a bottle and allowed to settle. The densities of the liquids are as follows:
X = 1.5 g/cm3
Y = 3.0 g/cm3
Z = 1.0 g/cm3
Draw a sketch to show the various layers into which the liquids settle.
(ii) The density of petrol is 0.9 g/cm3. Calculate the volume of 300 g of petrol.